文件操作-查看文件属性FileInfo
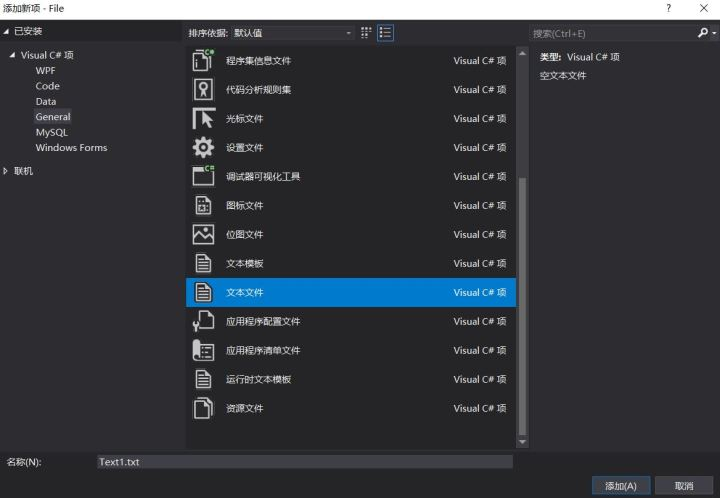
创建文本文件,并在其中编辑内容“Hello World!!!”。
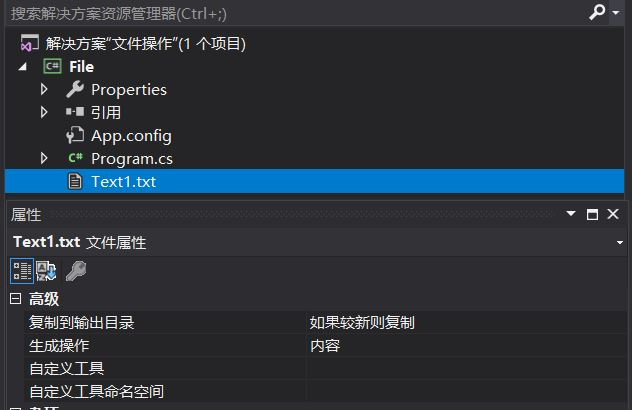
修改复制到输出目录选项为如果较新则复制。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 static void Main (string [] args { FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo("TextFile1.txt" ); Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Exists); Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Name); Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Length); Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Directory); Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.IsReadOnly); fileInfo.CopyTo("tt.txt" ); fileInfo.Delete(); FileInfo fileInfo1 = new FileInfo("TextFile2.txt" ); if (!fileInfo1.Exists) { using (fileInfo1.Create()) ; } fileInfo1.MoveTo("TextFile3.txt" ); Console.ReadKey(); } }
文件操作-文件夹操作DirectoryInfo
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(@"D:\Visual Studio Projects\FileManage\FileManageLearning\bin\Debug" ); DirectoryInfo directoryInfo1 = new DirectoryInfo("Text" ); if (!directoryInfo1.Exists){ directoryInfo1.Create(); } Console.WriteLine(directoryInfo.Name); Console.WriteLine(directoryInfo.Parent); Console.WriteLine(directoryInfo.Root); Console.WriteLine(directoryInfo.CreationTime); directoryInfo.CreateSubdirectory("AAA" );
使用File读写文件
创建一个文本文件(默认名为TextFile1),修改复制到输出目录选项为如果较新则复制(见开头)
输出每行文本 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { string [] s1 = File.ReadAllLines("TextFile1.txt" ); foreach (var item in s1) { Console.WriteLine(item); } string s = File.ReadAllText("TextFile1.txt" ); Console.Write(s); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
读取图片
将一个图片放在解决方案所在文件夹中,在Visual Studio中“添加现有项”为此图片,修改复制到输出目录选项为如果较新则复制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { byte [] s = File.ReadAllBytes("看手机.jpg" ); foreach (var b in s) { Console.Write(b); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
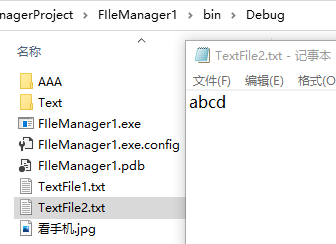
写入 1 2 File.WriteAllText("TextFile2.txt" , "abcd" );
1 2 File.WriteAllLines("TextFile3.txt" , new string [] { "我是" , "你" , "爸爸" });
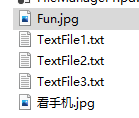
1 2 3 byte [] b = File.ReadAllBytes("看手机.jpg" );File.WriteAllBytes("Fun.jpg" , b);
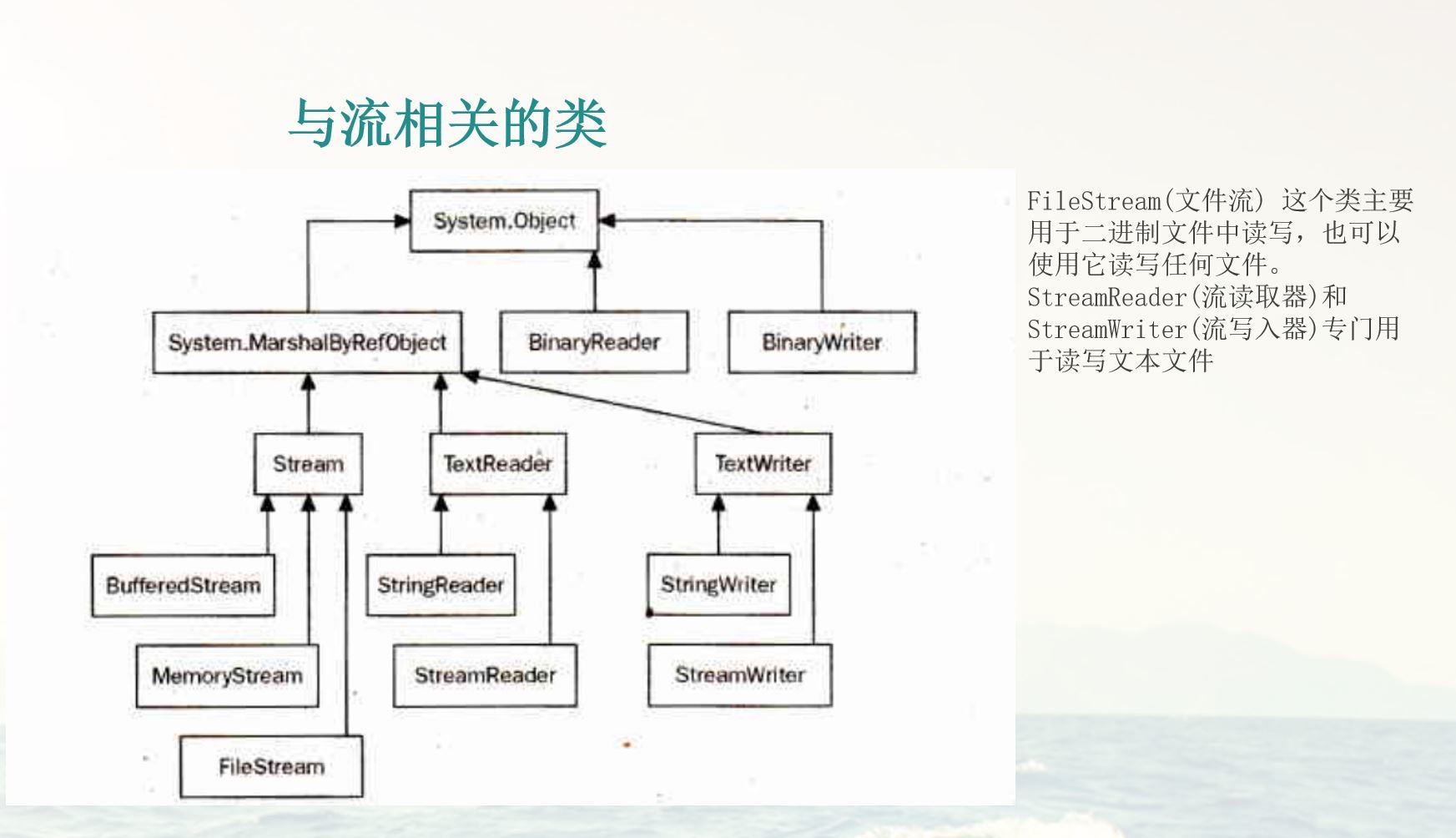
使用FileStream读写文件
FIleMode枚举成员表
成员
文件存在
文件不存在
Append
打开文件,流指向文件的末尾,只能与枚举FileAccess.Write联合使用
创建一个新文件。只能与枚举FileAccess.Write联合使用
Create
删除该文件,然后创建新文件
创建新文件
CreateNew
抛出异常
创建新文件
Open
打开现有的文件,流指向文件的开头
抛出异常
OpenOrCreate
打开文件,流指向文件的开头
创建新文件
Truncate
打开现有文件,清除其内容。流指向文件的开头,保留文件的初始创建日期
抛出异常
FileAccess枚举成员表
成员
说明
Read
打开文件,用于只读
Write
打开文件,用于只写
ReadWrite
打开文件,用于读写
FileStream类维护内部文件指针 ,该指针指向文件中进行下一次读写操作的位置。在大多数情况下,当打开文件时,它就指向文件的开始位置,但是此指针可以修改。这允许应用程序在文件的任何位置读写,随机访问文件,或直接跳到文件的特定位置上。当处理大型文件时,这非常省时,因为马上可以定位到正确的位置。
实现此功能的方法是Seek()方法,它有两个参数:第一个参数规定文件指针以字节为单位的移动距离。第二个参数规定开始计算的起始位置,用SeekOrigin枚举的一个值表示。Seek Origin枚举包含3个值:Begin、Current和End。
例如,下面的代码行将文件指针移动到文件的第8个字节,其起始位置就是文件的第1个字节:
1 aFile.Seek(8 ,SeekOrigin.Begin);
FileStream.Read()方法是从FileStream对象所指向的文件中访问数据的主要手段。这个方法从文件中读取数据,再把数据写入一个字节数组。它有三个参数:第一个参数是传输进来的字节数组,用以接受FileStream对象中的数据。第二个参数是字节数组中开始写入数据的位置。它通常是0,表示从数组开端向文件中写入数据。最后一个参数指定从文件中读出多少字节。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { FileStream fileStream = new FileStream("TextFile1.txt" , FileMode.Open); byte [] data = new byte [1024 ]; while (true ) { int length = fileStream.Read(data, 0 , data.Length); if (length == 0 ) { Console.WriteLine("读取结束" ); break ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { Console.Write(data[i] + " " ); } } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
注意显示的是字节值,并非是原文件内容。TextFile1的大小只有31字节,所以这里有31个byte值。
微软官方示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 using System;using System.IO;class Test { public static void Main (){ string pathSource = @"c:\tests\source.txt" ; string pathNew = @"c:\tests\newfile.txt" ; try { using (FileStream fsSource = new FileStream(pathSource, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { byte [] bytes = new byte [fsSource.Length]; int numBytesToRead = (int )fsSource.Length; int numBytesRead = 0 ; while (numBytesToRead > 0 ) { int n = fsSource.Read(bytes, numBytesRead, numBytesToRead); if (n == 0 ) break ; numBytesRead += n; numBytesToRead -= n; } numBytesToRead = bytes.Length; using (FileStream fsNew = new FileStream(pathNew, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { fsNew.Write(bytes, 0 , numBytesToRead); } } } catch (FileNotFoundException ioEx) { Console.WriteLine(ioEx.Message); } } }
读写图片 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { FileStream readStream = new FileStream("看手机.jpg" , FileMode.Open); FileStream writeStream = new FileStream("Fun.jpg" , FileMode.Create); byte [] data = new byte [1024 ]; while (true ) { int length = readStream.Read(data, 0 , data.Length); if (length == 0 ) { break ; } else { writeStream.Write(data, 0 , length); } } readStream.Close(); writeStream.Close(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
在读写图片这个示例中,data这个数组纯粹是个数据载体,它读多少写多少,所以我们每次都是从0开始
而在微软官方示例中,bytes数组是把整个文件都读完了再写,所以在方法中就使用了numBytesRead这个参数,防止每次都从0开始
使用StreamReader和StreamWriter读写文本文件
创建TextFile4,修改文件输出目录选项为如果较新则复制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader("TextFile4.txt" ); while (true ) { string str = streamReader.ReadLine(); if (str == null ) { break ; } else { Console.WriteLine(str); } } Console.WriteLine(streamReader.ReadToEnd()); streamReader.Close(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { StreamReader streamReader = new StreamReader("TextFile4.txt" ); while (true ) { int res = streamReader.Read(); if (res == -1 ) { break ; } else { Console.Write((char )res); } } streamReader.Close(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
输出的结果和上面一样,StreamReader.Read()将流中的下一个字符以int的形式返回,如果在流的末尾则返回-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 using System;using System.IO;namespace FIleManager1 { class Program { static void Main (string [] args { StreamWriter streamWriter = new StreamWriter("TextFile5.txt" ); while (true ) { string str = Console.ReadLine(); if (str == "q" ) { break ; } else { streamWriter.WriteLine(str); } } streamWriter.Close(); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
第一个xml文档示例 XML指可扩展标记语言。
XML被设计用来传输和存储数据。XML被设计用来结构化、存储以及传输信息。
XML不能做任何事情,它仅仅是包装在XML标签中的纯粹信息。我们需要编写软件或者程序,才能传送、接收和显示出这个文档。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> <note > <to > George</to > <from > John</from > <heading > Reminder</heading > <body > Don't forget the meeting!</body > </note >
XML文档规则,手写一个XML文档
在Visual Studio的解决方案资源管理器里面新建项,选择XML文件,注意修改属性为如果较新则复制
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <skills > <skill > <id > 2</id > <name lang ="cn" > 天下无双</name > <damege > 123</damege > </skill > <skill > <id > 3</id > <name lang ="cn" > 永恒零度</name > <damege > 93</damege > </skill > <skill > <id > 4</id > <name lang ="cn" > Xxxx</name > <damege > 400</damege > </skill > </skills >
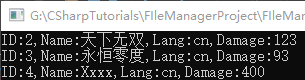
XML文档解析 创建一个skill类模型与XML对应,然后一层层的读出xml并赋值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 using System;using System.IO;using System.Xml;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace FIleManager1 { class Skill { public int ID { get ; set ; } public string Name { get ; set ; } public string Lang { get ; set ; } public int Damage { get ; set ; } public override string ToString () { return string .Format("ID:{0},Name:{1},Lang:{2},Damage:{3}" ,ID,Name,Lang,Damage); } } class Program { static void Main (string [] args { List<Skill> skillList = new List<Skill>(); XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument(); xmlDoc.Load("XMLFile1.xml" ); XmlNode rootNode = xmlDoc.LastChild; XmlNodeList skillNodeList = rootNode.ChildNodes; foreach (XmlNode skillNode in skillNodeList) { Skill skill = new Skill(); XmlNodeList fieldNodeList = skillNode.ChildNodes; foreach (XmlNode fieldNode in fieldNodeList) { if (fieldNode.Name == "id" ) { int id = Int32.Parse(fieldNode.InnerText); skill.ID = id; } else if (fieldNode.Name == "name" ) { string name = fieldNode.InnerText; skill.Name = name; skill.Lang = fieldNode.Attributes[0 ].Value; } else { skill.Damage = Int32.Parse(fieldNode.InnerText); } } skillList.Add(skill); } foreach (Skill skill in skillList) { Console.WriteLine(skill.ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
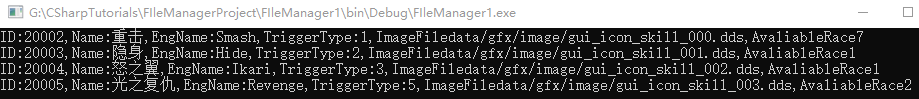
XML文档解析技能信息 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <SkillInfo > <SkillList > <Skill SkillID ="20002" SkillEngName ="Smash" TriggerType ="1" ImageFile ="data/gfx/image/gui_icon_skill_000.dds" AvailableRace ="7" > <Name > 重击</Name > </Skill > <Skill SkillID ="20003" SkillEngName ="Hide" TriggerType ="2" ImageFile ="data/gfx/image/gui_icon_skill_001.dds" AvailableRace ="1" > <Name > 隐身</Name > </Skill > <Skill SkillID ="20004" SkillEngName ="Ikari" TriggerType ="3" ImageFile ="data/gfx/image/gui_icon_skill_002.dds" AvailableRace ="1" > <Name > 怒之翼</Name > </Skill > <Skill SkillID ="20005" SkillEngName ="Revenge" TriggerType ="5" ImageFile ="data/gfx/image/gui_icon_skill_003.dds" AvailableRace ="2" > <Name > 光之复仇</Name > </Skill > </SkillList > </SkillInfo >
解析代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 using System;using System.IO;using System.Xml;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace FIleManager1 { class Skill { public int ID { get ; set ; } public string Name { get ; set ; } public string EngName { get ; set ; } public int TriggerType { get ; set ; } public string ImageFile { get ; set ; } public int AvaliableRace { get ; set ; } public override string ToString () { return string .Format("ID:{0},Name:{1},EngName:{2},TriggerType:{3},ImageFile{4},AvaliableRace{5}" ,ID,Name,EngName,TriggerType,ImageFile,AvaliableRace); } } class Program { static void Main (string [] args { List<Skill> skillList = new List<Skill>(); XmlDocument xmlDoc = new XmlDocument(); xmlDoc.Load("XMLFile2.xml" ); XmlNode skillListNode = xmlDoc.LastChild.FirstChild; XmlNodeList skillNodeList = skillListNode.ChildNodes; foreach (XmlNode skillNode in skillNodeList) { Skill skill = new Skill(); XmlElement ele = skillNode["Name" ]; skill.Name = ele.InnerText; XmlAttributeCollection col = skillNode.Attributes; skill.ID = int .Parse(col["SkillID" ].Value); skill.EngName = col["SkillEngName" ].Value; skill.TriggerType = int .Parse(col["TriggerType" ].Value); skill.ImageFile = col["ImageFile" ].Value; skill.AvaliableRace = int .Parse(col["AvailableRace" ].Value); skillList.Add(skill); } foreach (Skill skill in skillList) { Console.WriteLine(skill.ToString()); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
XmlNode、XmlElement、XmlAttribute、XmlText的区别 简单理解,XmlElement、XmlAttribute、XmlText都是XmlNode的一种,其中XmlElement既包括了XmlAttribute信息,又包括了XmlText信息
在使用时,声明这四种的哪一种似乎都一样,具体的区别待补充。
Json介绍
通过JSON官网进一步学习JSON JSON
书写JSON文本,引入JSON库文件 新建文本文件,但是按照Json的原则书写内容
1 2 3 4 5 [ { "id" : 2 , "name" : "happy tree" , "damage" : 123 } , { "id" : 3 , "name" : "sad glass" , "damage" : 123 } , { "id" : 4 , "name" : "blue garden" , "damage" : 123 } ]
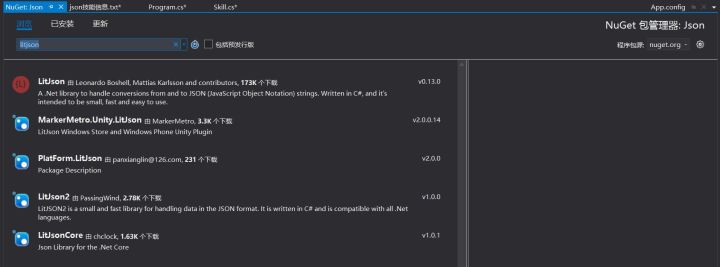
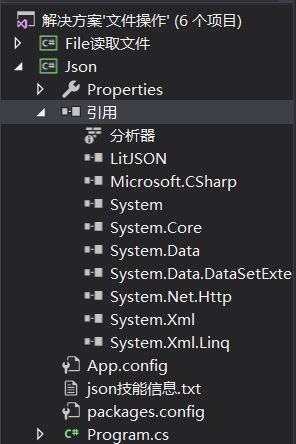
添加LitJson引用
使用JsonMapper解析Json数据 注意将文本文件的属性修改为如果较新则复制
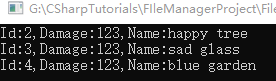
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using LitJson;using System.IO;namespace FileManager2 { class Skill { public int id; public int damage; public string name; public override string ToString () { return string .Format($"Id:{id} ,Damage:{damage} ,Name:{name} " ); } } class Program2 { static void Main (string [] args { List<Skill> skillList = new List<Skill>(); JsonData jsonData = JsonMapper.ToObject(File.ReadAllText("JsonFile1.txt" )); foreach (JsonData temp in jsonData) { Skill skill = new Skill(); JsonData idValue = temp["id" ]; JsonData nameValue = temp["name" ]; JsonData damageValue = temp["damage" ]; int id = int .Parse(idValue.ToString()); int damage = int .Parse(damageValue.ToString()); skill.id = id; skill.damage = damage; skill.name = nameValue.ToString(); skillList.Add(skill); } foreach (var item in skillList) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
使用JsonMapper跟泛型解析Json 可以进一步使用JsonMapper进行简化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 using System;using LitJson;using System.IO;namespace FileManager2 { class Skill { public int id; public int damage; public string name; public override string ToString () { return string .Format($"Id:{id} ,Damage:{damage} ,Name:{name} " ); } } class Program2 { static void Main (string [] args { Skill[] skillArray = JsonMapper.ToObject<Skill[]>(File.ReadAllText("JsonFile1.txt" )); foreach (var s in skillArray) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
或者
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static void Main (string [] args{ List<Skill> skillArray = JsonMapper.ToObject<List<Skill>>(File.ReadAllText("JsonFile1.txt" )); foreach (var s in skillArray) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.ReadLine(); }
Json实例应用 主角信息 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 { "Name" : "Xxx" , "Level" : 99 , "Age" : 18 , "SkillList" : [ { "id" : 2 , "name" : "天下无双" , "damage" : 123 } , { "id" : 3 , "name" : "天下无贼" , "damage" : 21 } , { "id" : 4 , "name" : "咫尺天涯" , "damage" : 900 } ] }
新添加Player类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 using System.Collections.Generic;namespace FileManager2 { class Player { public string Name { get ; set ; } public int Level { get ; set ; } public int Age { get ; set ; } public List<Skill> SkillList { get ; set ; } public override string ToString () { return string .Format($"Name:{Name} ,Level:{Level} ,Age:{Age} ,SkillList:{SkillList} " ); } } }
解析代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 using System;using LitJson;using System.IO;namespace FileManager2 { class Skill { public int id; public int damage; public string name; public override string ToString () { return string .Format($"Id:{id} ,Damage:{damage} ,Name:{name} " ); } } class Program2 { static void Main (string [] args { Player p = JsonMapper.ToObject<Player>(File.ReadAllText("JsonFile2.txt" )); Console.WriteLine(p); foreach (var temp in p.SkillList) { Console.WriteLine(temp); } Console.ReadLine(); } } }
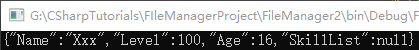
Json文本转换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 using System;using LitJsonnamespace FileManager2 { class Program2 { static void Main (string [] args { Player p = new Player(); p.Name = "Xxx" ; p.Level = 100 ; p.Age = 16 ; string json = JsonMapper.ToJson(p); Console.WriteLine(json); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
Json校检和Json在线编辑器 在线JSON校验格式化工具(Be JSON)
该网站可以使我们轻松的编辑Json文档
Excel操作
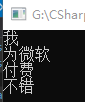
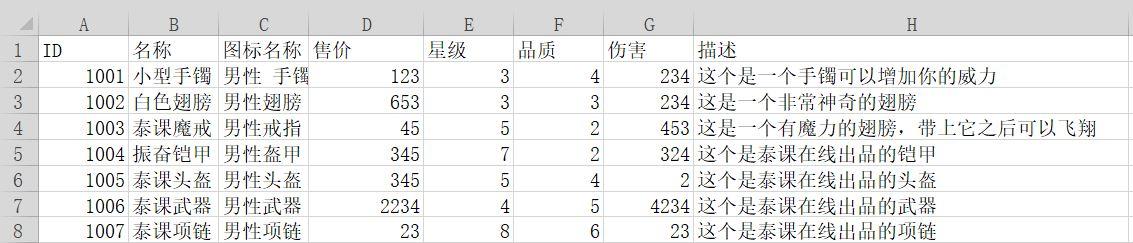
创建如下图所示的Excel(xls格式),复制到项目中并添加它,将其属性中的复制到输出目录选项为如果较新则复制。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 using System;using LitJson;using System.IO;using System.Data;using System.Data.OleDb;namespace FileManager2 { class Program2 { static void Main (string [] args { string fileName = "装备信息.xls" ; string connectionString = "Provider = Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;" + "Data Source = " + fileName + ";" + "; Extended Properties =\"Excel 8.0;HDR=YES;IMEX=1\"" ; OleDbConnection oleDbConnection = new OleDbConnection(connectionString); oleDbConnection.Open(); string sql = "select*from[Sheet1$]" ; OleDbDataAdapter oleDbDataAdapter = new OleDbDataAdapter(sql, oleDbConnection); DataSet dataSet = new DataSet(); oleDbDataAdapter.Fill(dataSet); oleDbConnection.Close(); DataTableCollection dataTableCollection = dataSet.Tables; DataTable table = dataTableCollection[0 ]; DataRowCollection dataRowCollection = table.Rows; foreach (DataRow row in dataRowCollection) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++) { Console.Write(row[i] + " " ); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }