使用协程分解复杂逻辑 在Unity中,协程可以处理一些异步任务。例如,假设某一个角色有“饱食度”和“困倦值”两个属性,这两个属性会不断衰减,当角色饿了会自己寻找食物,困了时会去睡觉。
不用状态机,借助协程解决:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 using System.Collections;using UnityEngine;namespace ACTBook { public class VillagerFSM : MonoBehaviour { public const float FATIGUE_DEFAULT_VALUE = 12f ; public const float SATIATION_DEFAULT_VALUE = 5f ; public const float FATIGUE_MIN_VALUE = 0.3f ; public const float SATIATION_MIN_VALUE = 0.2f ; [SerializeField ] Villager villager = null ; Coroutine mActionCoroutine; Coroutine mImportantActionCoroutine; void OnEnable () { villager.Satiation = SATIATION_DEFAULT_VALUE; villager.Fatigue = FATIGUE_DEFAULT_VALUE; StartCoroutine(Tick()); } IEnumerator Tick () { while (true ) { villager.Satiation = Mathf.Max(0 , villager.Satiation - Time.deltaTime); villager.Fatigue = Mathf.Max(0 , villager.Fatigue - Time.deltaTime); if (villager.Satiation <= SATIATION_MIN_VALUE && mActionCoroutine == null ) { mActionCoroutine = StartCoroutine(EatFood()); } if (villager.Fatigue <= FATIGUE_MIN_VALUE && mImportantActionCoroutine == null ) { if (mActionCoroutine != null ) { StopCoroutine(mActionCoroutine); mActionCoroutine = null ; } mImportantActionCoroutine = StartCoroutine(Sleep()); mActionCoroutine = mImportantActionCoroutine; } yield return null ; } } IEnumerator EatFood () { Debug.Log("开始寻找食物!" ); yield return villager.Eat(() => { Debug.Log("恢复饱食度!" ); villager.Satiation = SATIATION_DEFAULT_VALUE; }); mActionCoroutine = null ; } IEnumerator Sleep () { Debug.Log("开始睡觉!" ); yield return villager.Sleep(() => { Debug.Log("恢复精力!" ); villager.Fatigue = FATIGUE_DEFAULT_VALUE; }); mActionCoroutine = null ; mImportantActionCoroutine = null ; } } }
一些非常重要的角色或关卡逻辑,如触发剧情的村民,结合协程进行Hardcode(逻辑写死)处理非常高效。通常在Unity开发中这些根据剧情需要“写死”的角色逻辑的类命名也很简单,如NPC1001.cs、NPC1002.cs等。这些脚本不允许存在复用与依赖 。
关于协程的执行顺序参考协程的嵌套和调用模式 ,协程代码块内部的代码是按顺序依次执行的,而在外部调用协程的代码块是一次性执行的。要注意理解这种类似多线程代码的执行顺序。
在本案例的代码中还附带了villager自动寻路的业务逻辑,在这里贴出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 using System;using System.Collections;using UnityEngine;namespace ACTBook { public class Villager : MonoBehaviour { const float DOT_CHECK_ANGLE = 45f ; const int MOVE_ERROR_MAX = 20000 ; const float MOVE_IN_RANGE_EPS = 0.001f ; [SerializeField ] SpriteRenderer spriteRenderer = null ; [SerializeField ] Sprite sideSprite = null ; [SerializeField ] Sprite upSprite = null ; [SerializeField ] Sprite downSprite = null ; [SerializeField ] float moveSpeed = 0.5f ; [SerializeField ] Transform[] toEatPathArray = null ; [SerializeField ] Transform[] toSleepPathArray = null ; public float Satiation { get ; set ; } public float Fatigue { get ; set ; } public IEnumerator Eat (Action onAte ) { yield return MoveTo (Array.ConvertAll(toEatPathArray, m => m.position ), moveSpeed) yield return new WaitForSeconds (1f onAte?.Invoke(); var pointsReverse = Array.ConvertAll(toEatPathArray, m => m.position); Array.Reverse(pointsReverse); yield return MoveTo (pointsReverse, moveSpeed ) } public IEnumerator Sleep (Action onSlept ) { yield return MoveTo (Array.ConvertAll(toSleepPathArray, m => m.position ), moveSpeed) yield return new WaitForSeconds (1f onSlept?.Invoke(); var pointsReverse = Array.ConvertAll(toSleepPathArray, m => m.position); Array.Reverse(pointsReverse); yield return MoveTo (pointsReverse, moveSpeed ) } IEnumerator MoveTo (Vector3[] pathPointArray, float speed ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < pathPointArray.Length; i++) { var item = pathPointArray[i]; var pointReferenceDir = Vector3.forward; if (i > 0 ) pointReferenceDir = pathPointArray[i] - pathPointArray[i - 1 ]; else pointReferenceDir = pathPointArray[i] - transform.position; var dot = 1f ; var isInRadius = false ; var errorCount = 0 ; var moveDirection = (item - transform.position).normalized; if (moveDirection.normalized != Vector3.zero) ChangeDirectionSprite(moveDirection); do { if (errorCount > MOVE_ERROR_MAX) { Debug.LogError("Path Move Looping Error!" ); break ; } errorCount++; transform.position += moveDirection * Time.deltaTime * speed; var referenceDirection = (item - transform.position).normalized; dot = Vector3.Dot(pointReferenceDir.normalized, referenceDirection); isInRadius = Vector3.Distance(item, transform.position) <= MOVE_IN_RANGE_EPS; yield return null ; } while (dot > 0 && !isInRadius); } } void ChangeDirectionSprite (Vector3 direction ) { if (DotCheck(direction, new Vector3(0f , 1f , 0f ))) { spriteRenderer.sprite = upSprite; spriteRenderer.transform.localScale = new Vector3(1f , 1f , 1f ); } else if (DotCheck(direction, new Vector3(0f , -1f , 0f ))) { spriteRenderer.sprite = downSprite; spriteRenderer.transform.localScale = new Vector3(1f , 1f , 1f ); } else if (DotCheck(direction, new Vector3(1f , 0f , 0f ))) { spriteRenderer.sprite = sideSprite; spriteRenderer.transform.localScale = new Vector3(1f , 1f , 1f ); } else if (DotCheck(direction, new Vector3(-1f , 0f , 0f ))) { spriteRenderer.sprite = sideSprite; spriteRenderer.transform.localScale = new Vector3(-1f , 1f , 1f ); } } bool DotCheck (Vector3 srcDir, Vector3 compareDir ) { var dot = Vector3.Dot(srcDir, compareDir); var acos = Mathf.Acos(dot); var deg = acos * Mathf.Rad2Deg; return deg < DOT_CHECK_ANGLE; } } }
自定义插值公式 很多时候使用DOTween等一些插值插件来处理相关需求,但更多时候需要更灵活的插值处理,如发射导弹,释放火球等。
插值按数值类型分为整型和浮点型,按照应用分帧数相关类型和帧数无关类型。
Unity中的Lerp型函数
Lerp的本质是返回量个值之间的线性插值:以Vector3.Lerp为例
Unity - Scripting API: Vector3.Lerp (unity3d.com)
public static Vector3 Lerp(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float t);
在两点之间进行线性插值。 通过插值 t 在点 a 和 b 之间进行插值。参数 t 被限制在 [0, 1] 范围内。这最常用于沿着两个端点之间的一条线找到一个点(例如,在这些点之间逐渐移动一个对象)。
返回的值等于 a + (b - a) * t(也可以写成 a * (1-t) + b*t)。
当 t = 0 时,Vector3.Lerp(a, b, t) 返回 a。
当 t = 1 时,Vector3.Lerp(a, b, t) 返回 b。
当 t = 0.5 时,Vector3.Lerp(a, b, t) 返回 a 和 b 之间的中间点。
官方案例1
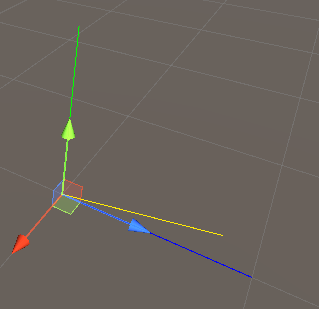
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 using UnityEngine;public class VectorLerpTest : MonoBehaviour { public int interpolationFramesCount = 45 ; int elapsedFrames = 0 ; void Update () { float interpolationRatio = (float )elapsedFrames / interpolationFramesCount; Vector3 interpolatedPosition = Vector3.Lerp(Vector3.up, Vector3.forward, interpolationRatio); elapsedFrames = (elapsedFrames + 1 ) % (interpolationFramesCount + 1 ); Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, Vector3.up, Color.green); Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, Vector3.forward, Color.blue); Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, interpolatedPosition, Color.yellow); } }
官方案例2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 using UnityEngine;public class VectorLerpTest : MonoBehaviour { public Transform startMarker; public Transform endMarker; public float speed = 1.0F ; private float startTime; private float journeyLength; void Start () { startTime = Time.time; journeyLength = Vector3.Distance(startMarker.position, endMarker.position); } void Update () { float distCovered = (Time.time - startTime) * speed; float fractionOfJourney = distCovered / journeyLength; transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(startMarker.position, endMarker.position, fractionOfJourney); } }
Unity - Scripting API: Vector3.Slerp (unity3d.com)
Unity - Scripting API: Vector3.LerpUnclamped (unity3d.com)
Unity - Scripting API: Mathf.SmoothDampAngle (unity3d.com)
Unity中的SmoothDamp型函数
SmoothDamp是一种缓动型插值:以Vector3.SmoothDamp为例
public static Vector3 SmoothDamp(Vector3 current, Vector3 target, ref Vector3 currentVelocity, float smoothTime, float maxSpeed = Mathf.Infinity, float deltaTime = Time.deltaTime);
smoothTime: 大约需要达到目标所需的时间。较小的值将更快地达到目标。
maxSpeed: (可选)允许您限制最大速度。
deltatime: 自上次调用此函数以来的时间。默认情况下是Time.deltaTime。
随着时间的推移逐渐将向量更改为期望的目标。
向量被一些类似弹簧阻尼器的函数平滑,它永远不会过冲。最常见的用途是平滑跟随相机。
官方案例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 using UnityEngine;public class SmoothDampTest : MonoBehaviour { public Transform target; public float smoothtime = 0.3f ; private Vector3 velocity = Vector3.zero; void Update () { Vector3 targetPosition = target.TransformPoint(new Vector3(0 , 5 , -10 )); transform.position = Vector3.SmoothDamp(transform.position, targetPosition, ref velocity, smoothtime); } }
target.TransformPoint(new Vector3(0, 5, -10));指的是无论target的本地坐标在哪里,返回的targetPosition的值一直在相对于target世界坐标(0,5,-10)的位置
运行时移动target对象,可以发现物体在缓动跟随target
Quicken类型 这是书中提到的一种插值函数,是将Lerp函数的第三个参数传入时间的平方实现
Quicken是一种帧数相关的插值类型
Quicken类型非常简单实用,而且不会造成太多开销。可以修改为t^n进行微调,其中,t是一个0~1之间的值。
这种插值也可以运用在非物体运动中。例如,PostProcessingStack插件的Bloom后处理效果,实现了超出颜色范围的平滑过渡处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 using UnityEngine;namespace ACTBook { public class Tween3 : MonoBehaviour { const float TIME = 3f ; const float DISTANCE = 3f ; const float SMOOTH_TIME = 0.2f ; Vector3 mVelocity; void Update () { var t = Mathf.Repeat(Time.time, TIME) / TIME; var quicken_t = t * t; transform.localPosition = Vector3.Lerp(new Vector3(0f , 0f , 0f ), new Vector3(DISTANCE, 0f , 0f ), quicken_t); } } }
EaseInOut类型 下面再介绍一种较为常用的EaseInOut插值类型:
1 2 3 t = (t - 1f) * (t - 1f) * (t - 1f) + 1f t = t * t
第一行的逻辑表现更类似于SmoothDamp那种较为平滑的运动,第二行加入EaseIn插值使其达到淡入淡出的插值效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 using UnityEngine;namespace ACTBook { public class Tween4 : MonoBehaviour { const float TIME = 3f ; const float DISTANCE = 3f ; void Update () { var t = Mathf.Repeat(Time.time, TIME) / TIME; t = (t - 1f ) * (t - 1f ) * (t - 1f ) + 1f ; t = t * t; transform.localPosition = Vector3.Lerp(new Vector3(0f , 0f , 0f ), new Vector3(DISTANCE, 0f , 0f ), t); } } }
消息模块设计(不依赖Unity) 实现一个简单的消息管理器:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;using UnityEngine;using System;public class MessageManager { static MessageManager m_Instance; public static MessageManager Instance => m_Instance ??= new MessageManager(); Dictionary<string , Action<object []>> m_MessageDict = new Dictionary<string , Action<object []>>(32 ); Dictionary<string , object []> m_DispatchCacheDict = new Dictionary<string , object []>(16 ); private MessageManager () public void Subscribe (string message,Action<object []> action { Action<object []> value = null ; if (m_MessageDict.TryGetValue(message,out value )) { value += action; m_MessageDict[message] = value ; } else { m_MessageDict.Add(message, action); } } public void Unsubscribe (string message { m_MessageDict.Remove(message); } public void Dispatch (string message,object [] args = null ,bool addToCache = false { if (addToCache) { m_DispatchCacheDict[message] = args; } else { Action<object []> value = null ; if (m_MessageDict.TryGetValue(message, out value )) value (args); } } public void ProcessDispatchCache (string message { object [] value = null ; if (m_DispatchCacheDict.TryGetValue(message,out value )) { Dispatch(message, value ); m_DispatchCacheDict.Remove(message); } } }
以上是一个简单的消息管理器的实现,使用单例进行调用。除了订阅(Subscribe)、取消订阅(Unsubscribe),还需要处理延迟分发(Dispatch)的情况。假设玩家在游戏中获得新装备,系统会发送消息通知背包面板去显示第二个页签上的红点提示,但此时背包面板尚未创建怎么办,使用延迟消息先把消息推送到缓存中,需要时自行调用即可。
模块间的管理与协调 首先来说一下模块的单例,单例一般可以分为MonoBehaviour单例和常规单例,MonoBehaviour单例会在运行时创建一个GameObject对象并置于DontDestroyOnLoad场景中,另外,基于MonoBehaviour的单例需要注意销毁的问题。
下面来看一个例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;using UnityEngine;public class MonoBehaviourSingleton : MonoBehaviour { static bool m_IsDestroying; static MonoBehaviourSingleton m_Instance; public static MonoBehaviourSingleton Instance { get { if (m_IsDestroying) return null ; if (!m_Instance) { m_Instance = new GameObject("#MonoBehaviourSingleton#" ).AddComponent<MonoBehaviourSingleton>(); DontDestroyOnLoad(m_Instance.gameObject); } return m_Instance; } } private void OnDestroy () { m_IsDestroying = true ; } }
我们在其中加入m_IsDestroying变量,防止对已经销毁的单例进行重复创建。(所有静态变量会一直记着)
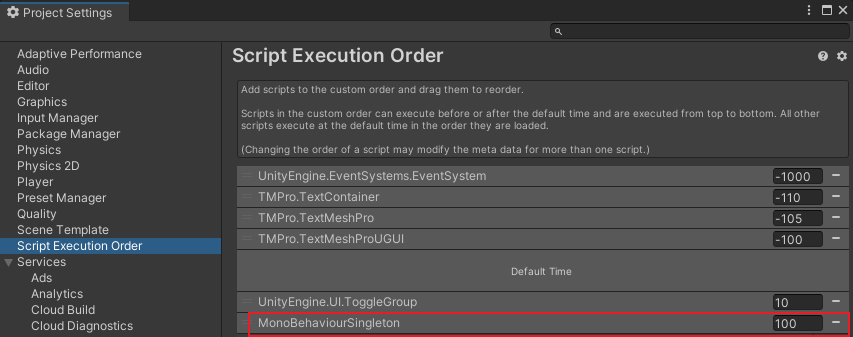
在模块初始化时还需要考虑其相互依赖关系,可以直接在Project Settings里面修改Script Execution Order