1. 反射和特性-Type类,用来访问单个类 什么是元数据,什么是反射
程序是用来处理数据的,文本和特性都是数据,而我们程序本身(类的定义和BCL中的类)这些也是数据。
有关程序及其类型的数据被称为元数据(metadata),它们保存在程序的程序集中。
程序在运行时,可以查看其他程序集或其本身的元数据。一个运行的程序查看本身的元数据或者其他程序集的元数据的行为叫做反射。
下面我们来学习如何使用Type类来反射数据,以及如何使用特性来给类型添加元数据。System.Reflection命名空间下
BCL:Basic Class Library 基础类库
Type类 预定义类型(int long 和 string等),BCL中的类型(Console,IEnumerable等)和程序员自定义类型(MyClass、MyDel等)。每种类型都有自己的成员和特性。
BCL声明了一个叫做Type的抽象类,他被设计用来取得类型的成员和特性。使用这个类的对象能让我们获取程序使用的类型信息。
由于Type是抽象类,因此不能利用它去实例化对象。关于Type的重要事项如下:
对于程序中用到的每一个class,CLR都会创建一个包含这个类型信息的Type类
程序中用到的每一个class都会关联到独立的Type类的对象。
不管创建的类型有多少个实例,只有一个Type对象会关联到所有实例
System.Type类部分成员
成员 成员类型 描述
Name属性
返回class名字
Namespace属性
返回包含class的命名空间
Assembly属性
返回声明class的程序集
GetFields方法
返回class内的字段列表
GetProperties方法
返回class内的属性列表
GetMethods方法
返回class内的方法列表
获取Type对象 获取Type对象有两种方式
1、
1 2 Type t = myInstance.GetType();
2、
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Type t = typeof (ClassName); FieldInfo[] fi = t.GetFields(); foreach (FieldInfo f in fi){ Console.WriteLine(f.Name + "" ); }
 class myClassForReflect
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class myClassForReflect { private int id; private int age; public int number; public string Name1 { get ; set ; } public string Name2 { get ; set ; } public string Name3 { get ; set ; } public void Test1 () public void Test2 () }
class ReflectionTest1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class ReflectionTest1 { static void Main (string [] args { myClassForReflect myClassForReflect = new myClassForReflect(); Type mytype = myClassForReflect.GetType(); Console.WriteLine(mytype.Name); Console.WriteLine(mytype.Namespace); Console.WriteLine(mytype.Assembly); FieldInfo[] fieldinfos = mytype.GetFields(); foreach (var item in fieldinfos) { Console.Write(item.Name + " " ); } Console.WriteLine(); PropertyInfo[] propertyInfos = mytype.GetProperties(); foreach (var item in propertyInfos) { Console.Write(item.Name + " " ); } Console.WriteLine(); MethodInfo[] methodInfos = mytype.GetMethods(); foreach (var item in methodInfos) { Console.Write(item.Name + " " ); } } }
2. 反射和特性-Assembly程序集类,用来访问此类所属的程序集 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class ReflectionTest1 { static void Main (string [] args { myClassForReflect myClassForReflect = new myClassForReflect(); Assembly assembly = myClassForReflect.GetType().Assembly; Console.WriteLine(assembly.FullName); Type[] types = assembly.GetTypes(); foreach (var item in types) { Console.WriteLine(item); } } }
Assembly类 Assembly类在System.Reflection命名空间中定义,它允许访问给定程序集的元数据,它也包含了以加载和执行程序集
如何加载程序集
1、根据程序集的名字加载程序集,它会在本地目录和全局程序集缓存目录查找符合名字的程序集
1 Assembly assembly1 = Assembly.Load("SomeAssembly" );
2、直接在指定路径加载程序集
1 Assembly assembly2 = Assembly.LoadFrom(@"C:\xx\xx\xx\SomeAssembly.dll" );
Assembly对象的使用 1、获取程序集的全名
1 string name = assembly1.FullName;
2、遍历程序集中定义的类型
1 2 3 4 5 Type[] types = theAssembly.GetTypes(); foreach (Type definedType in types){ }
3、遍历程序集中定义的特性
1 Attribute[] definedAttributes = Attribute.GetCustomAttributes(someAssembly);
3. Obsolete特性 什么是特性?
特性(attribute)是一种允许我们向程序的程序集增加元数据 的语言结构。它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类 。
将应用了特性的程序结构叫做目标
设计用来获取和使用元数据的程序(对象浏览器)叫做特性的消费者
DotNet预定了很多特性,我们也可以声明自定义特性
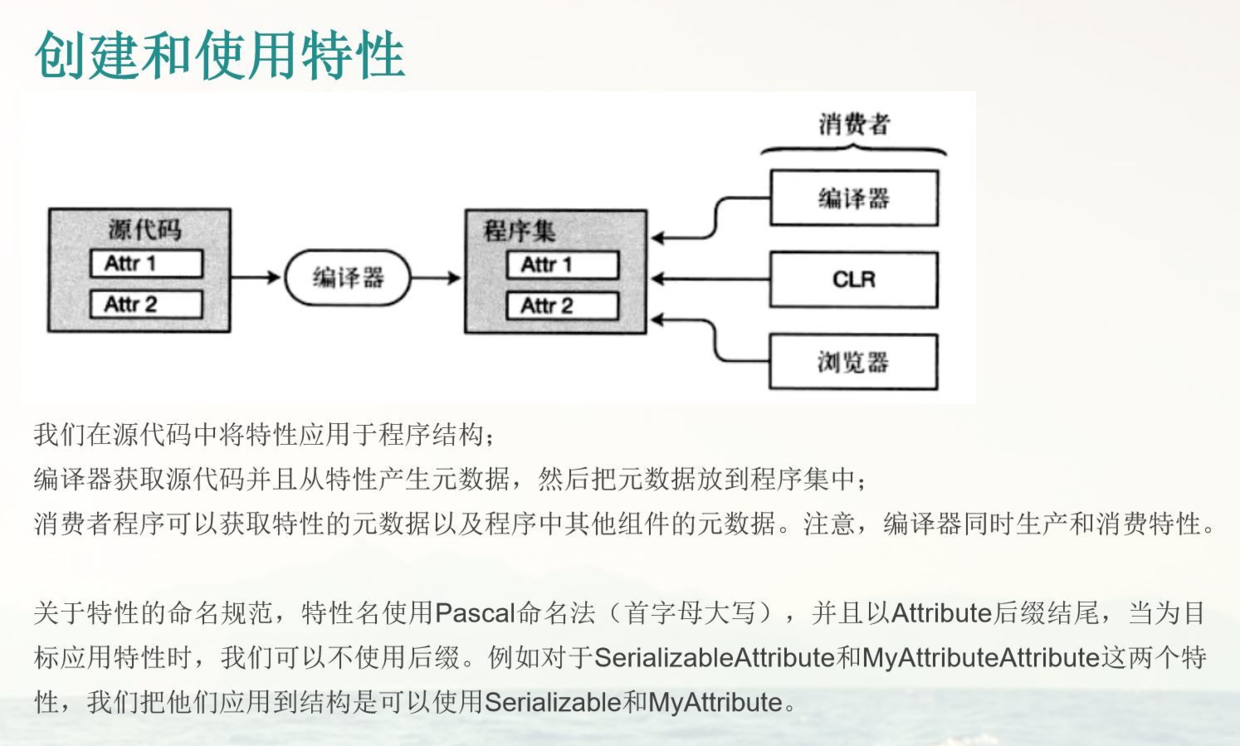
创建和使用特性 我们在源代码中将特性应用于程序结构;
编译器获取源代码并且从特性产生元数据,然后把元数据放到程序集中;
消费者程序可以获取特性的元数据以及程序其他组件的元数据。注意,编译器同时生产和消费特性。
应用特性 先看看如何应用特性。特性的目的是告诉编译器把程序结构的某组元数据嵌入程序集。我们可以通过把特性应用到结构来实现。
在结构前放置特性片段来应用特性;
特性片段被方括号包围,特性片段包括特姓名和特性的参数列表;
应用了特性的结构称为特性装饰
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [Serializable ] public class MyClass { } [MyAttribute("Simple class" ,"Version 3.57" ] public class MyClass { }
Obsolete特性->.Net预定义特性 一个程序可能在其生命周期经历多次发布,而且很可能延续多年。在程序服务时长的后半部分,程序员经常需要编写类似功能的新方法替换老方法。出于多种原因,你可能不再使用那些老方法。
旧的方法不能删除,因为有些旧代码也使用旧的方法,这是就使用Obsolete特性将程序结构标注为过期的,并且在代码编译时,显示有用的警告信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Program {[Obsolete("Use method SuperPrintOut" ) ] static void PrintOut (string str Console.WriteLine(str); } [Obsolete("Use method SuperPrintOut" ,true) ] static void PrintOut (string str Console.WriteLine(str); } static void Main (string [] args PrintOut("Start of Main" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 namespace Attributes_Test { [Obsolete("THIS IS OLD METHOD" ) ] static void OldMethod () { Console.WriteLine("I'm Old." ); } [Obsolete("THIS IS OLD METHOD" ,true) ] static void OldMethodGetRid () { Console.WriteLine("I'm Old,Quit" ); } static void Main (string [] args { OldMethod(); OldMethodGetRid(); NewMethod(); } }
4. Conditional特性 Conditonal特性允许我们包括或取消特定方法的所有调用。为方法声明应用Conditional特性并把预编译指令作为参数来使用。
定义方法的CIL代码本身总是会包含在程序集中,只是调用代码会被插入或忽略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #define DoTrace class Program {[Conditional("DoTrace" ) ] static void TraceMessage (string str Console.WriteLine(str); } static void Main () TraceMessage("Start of Main" ); Console.WriteLine("Doing work in Main" ); TraceMessage("End of Main" ); } }
需要引用System.Diagnostics命名空间
使用宏定义#define时要放在using前面
不使用宏定义时,conditional所在的属性或方法会被编译在程序集中 (与#if区分),但是会被插入或忽略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #define ForCondition using System;using System.Diagnostics;namespace Attributes_Test { class AttributeTest1 { [Conditional("ForCondition" ) ] static void NewMethod () { Console.WriteLine("I'm Fresh" ); } static void Main (string [] args { NewMethod(); } } }
5. 调用者信息特性 调用者信息特性可以访问文件路径,代码行数,调用成员的名称等源代码信息。
这个三个特性名称为CallerFilePath、CallerLineNumber和CallerMemberName
这些特性只能用于方法中的可选参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void PrintOut (string message,[CallerFilePath]string filename="" ,[CallerLineNumber]int lineNumber = 0 ,[CallerMemberName]string callingMember="" { Console.WriteLine("Message:" + message); Console.WriteLine("Line:" + lineNumber); Console.WriteLine("Called from:" + callingMember); }
使用using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 using System;using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;namespace Attributes_Test { class AttributeTest1 { static void ForCaller (string str, [CallerFilePath] string callerFile = "" , [CallerLineNumber] int callerLnum = 0 , [CallerMemberName] string callerMem = "" ) { Console.WriteLine(str); Console.WriteLine(callerFile); Console.WriteLine(callerLnum); Console.WriteLine(callerMem); } static void Main (string [] args { ForCaller("123" ); } } }
6. DebuggerStepThrough特性 我们在单步调试代码的时候,常常希望调试器不要进入某些方法。我们只想执行该方法,然后继续调试下一行。DebuggerStepThrough特性告诉调试器在执行目标代码时不要进入该方法调试。有些方法小并且毫无疑问是正确的,在调试时对其反复单步调试只能徒增烦恼。要小心使用该特性,不要排除了可能出现bug的代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 using System;using System.Diagnostics;using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;namespace _015_特性{ class Program { [DebuggerStepThrough ] static void PrintOut (string str,[CallerFilePath] string fileName="" , [CallerLineNumber] int lineNumber=0 ,[CallerMemberName] string methodName ="" ) { Console.WriteLine(str); Console.WriteLine(fileName); Console.WriteLine(lineNumber); Console.WriteLine(methodName); } static void Main (string [] args PrintOut("123" ); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
7. 创建自定义特性 声明自定义特性 特性作为一种需要嵌入的代码片段,一般独立性很强,需要一定的保护。
声明一个特性类和声明其他类一样。有下面的注意事项:
特性类都派生自System.Attribute
特性类需要以Attribute作为名字结尾
安全起见,一般特性类需要使用sealed关键字限定
特性类声明如下:
1 public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute : System.Attribute {}
特性类的公共成员可以是:字段,属性,构造函数。其余的都是私有的不可访问的,用来保证特性的独立性。
构造函数 特性类的构造函数的声明跟普通类一样,如果不写的话系统会提供默认构造函数,可以进行重载。
构造函数的调用
[MyAttribute("a value")] 调用特性类的带有一个字符串的构造函数
[MyAttribute("a value","Mackel")] 调用特性类的带有两个字符串的构造函数
构造函数的实参,必须是在编译期间能确定值的常量表达式。如果调用的是无参的构造函数,那么后面的括号可以不写。
自定义特性一般遵守的规范
特性类应该表示目标结构的一些状态
如果特性需要某些字段,可以通过包含具有位置参数的构造函数来收集数据,可选字段可以采用命名参数按需初始化
除了属性之外,不要实现公共方法和其他函数成员,特性方法只在被声明它的地方起作用
为了更安全,把特性类声明为sealed
在特性声明中使用AttributeUsage来指定特性目标组
限定特性的使用 有一个很重要的预定义特性可以用来应用到自定义特性上,那就是AttributeUsage特性,我们可以使用它来限制特性使用在某个目标类型上。
例如,如果我们希望自定义特性MyAttribute只能应用到方法上,那么可以用如下形式使用AttributeUsage:
1 2 3 [AttributeUsage(AttributeTarget.Method) ] public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute : System.Attribute {
AttributeUsage有三个重要的公共属性:
属性 功能
ValidOn保存特性能应用到的目标类型的列表,构造函数的第一个参数就是AttributeTarget类型的枚举值
Inherited一个布尔值,它指示特性是否会被特性类所继承,默认为true
AllowMultiple是否可以多个特性的实例应用到一个目标上,默认为FALSE
访问特性(消费特性) 1、我们可以使用IsDefined方法来,通过Type对象可以调用这个方法,来判断这个类上是否应用了某个特性
1 2 3 bool isDefined = t.IsDefined(typeof (AttributeClass),false )
2、
1 2 3 4 object [] attArray = t.GetCustomAttributes(false );
  MyTestAttribute类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 using System;using System.Net;namespace _015_特性 { [AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class) ] sealed class MyTestAttribute : System.Attribute { public string Description { get ; set ; } public string VersionNumber { get ; set ; } public int ID { get ; set ; } public MyTestAttribute (string des { this .Description = des; } } }
Program类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 using System;namespace _015_特性{ [MyTest("简单的特性类" ,ID = 100) ] class Program { static void Main (string [] args Type type = typeof (Program); object [] array = type.GetCustomAttributes(false ); MyTestAttribute mytest = array[0 ] as MyTestAttribute; Console.WriteLine(mytest.Description); Console.WriteLine(mytest.ID); Console.ReadKey(); } } }